The bigPCAcpp package provides high performance
principal component analysis (PCA) routines specialised for
bigmemory::big.matrix objects. It keeps data in bigmemory
allocations from ingestion through eigendecomposition so that very large
matrices can be analysed without copying them into base R matrices. In
addition to the PCA core, the package offers streaming helpers that
write scores, loadings, correlations, and contributions back into
file-backed big.matrix targets for integration with
downstream pipelines.
Beyond classical PCA, the package ships with scalable SVD tools that can process file-backed matrices block by block, and it includes robust PCA and robust SVD routines that temper the influence of outliers while remaining compatible with bigmemory workflows. For exploratory work on large batches, a scalable PCA interface lets users extract leading components without reading the full matrix into memory.
These workflows make it possible to analyse data sets that exceed the available RAM while keeping numerical stability through double-precision accumulation and LAPACK eigen decompositions. Current features include
big.matrix
inputs,bigmemory, andYou can install the development version of bigPCAcpp from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("fbertran/bigPCAcpp")If you prefer a local source install, clone the repository and run:
R CMD build bigPCAcpp
R CMD INSTALL bigPCAcpp_0.9.0.tar.gzThe package defines several options to control numerical tolerances
and workspace allocation. They are prefixed with bigPCAcpp.
and include:
| Option | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
bigPCAcpp.block_size |
1000L |
Number of rows processed in each block when streaming scores through BLAS. |
bigPCAcpp.center_scale_epsilon |
1e-8 |
Lower bound applied when rescaling columns to avoid division instabilities. |
bigPCAcpp.progress |
FALSE |
Emit progress updates when computing PCA on long-running jobs. |
All options can be changed with options() at runtime.
For example, options(bigPCAcpp.block_size = 5000L)
increases the streaming block size.
The examples below demonstrate the bigmemory workflow and compare the
results with base R’s prcomp() implementation.
library(bigmemory)
library(bigPCAcpp)
# Allocate a 1,000 x 25 big.matrix with simulated values
n <- 1000
p <- 25
bm <- bigmemory::big.matrix(n, p, type = "double")
bm[,] <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), nrow = n)
# Run PCA and extract eigenvalues and rotation
res <- pca_bigmatrix(bm, center = TRUE, scale = TRUE)
res$eigenvalues
#> [1] 1.2772679 1.2549573 1.2261127 1.2200832 1.2029447 1.1372111 1.1116603 1.0863140 1.0612750
#> [10] 1.0430975 1.0251884 1.0036304 0.9922516 0.9661366 0.9511738 0.9342366 0.9118102 0.8894958
#> [19] 0.8861798 0.8662711 0.8326502 0.8234052 0.7850452 0.7762024 0.7353990
res$importance
#> NULL
res$rotation[1:5, 1:3]
#> [,1] [,2] [,3]
#> [1,] -0.13665626 -0.19398781 0.3217218
#> [2,] -0.07597561 0.09425838 0.1678119
#> [3,] 0.08992670 0.00729943 0.2609075
#> [4,] 0.10200029 -0.28583284 0.2290518
#> [5,] 0.19534252 0.32324433 0.1690638
# Generate PCA scores in bigmemory storage
scores <- bigmemory::big.matrix(
nrow = n,
ncol = 3,
type = "double"
)
(pca_scores_bigmatrix(
bm,
res$rotation,
center = res$center,
scale = res$scale
))[1:6,1:6]
#> [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6]
#> [1,] 2.81870347 -0.06337779 1.99072631 -0.5920623 -1.6703024 1.6483439
#> [2,] -0.35747573 -0.80297261 -1.07285346 0.5123663 -1.4595653 0.5980145
#> [3,] -0.78310002 0.24236085 0.46701646 -0.2727803 0.4929943 2.2777379
#> [4,] 1.45650763 -0.74008842 -2.57891649 0.1402697 1.5748613 1.1219994
#> [5,] -1.56142789 -0.68169732 -0.01681349 0.1119421 -0.9571047 -1.0961306
#> [6,] 0.05141656 -0.91365588 0.30322391 -1.4171899 -0.2089137 -2.3574471
# Compare sum of absolute values with prcomp()
pr <- prcomp(bm[], center = TRUE, scale = TRUE)
sum(abs(abs(pr$rotation[, 1:3])-abs(res$rotation[, 1:3])))<10^(-6)
#> [1] TRUEpca_bigmatrix() can also focus on a subset of leading
components while streaming the results into file-backed matrices. The
following snippet stores the first four principal components and keeps a
running summary of their scores.
library(bigmemory)
library(bigPCAcpp)
set.seed(2025)
bm <- bigmemory::big.matrix(nrow = 1500, ncol = 40, type = "double")
bm[,] <- matrix(rnorm(1500 * 40), nrow = 1500)
# Request only the first four components
top_pca <- pca_bigmatrix(bm, center = TRUE, scale = TRUE, ncomp = 4)
top_pca$sdev
#> [1] 1.141546 1.124998 1.119607 1.109924
# Stream the corresponding scores into a file-backed allocation
path <- tempfile(fileext = ".bin")
desc <- paste0(path, ".desc")
scores_fb <- bigmemory::filebacked.big.matrix(nrow = nrow(bm), ncol = 4,
type = "double", backingfile = basename(path), backingpath =
dirname(path), descriptorfile = basename(desc)
)
pca_scores_stream_bigmatrix(
bm,
scores_fb,
top_pca$rotation[, 1:4],
center = top_pca$center,
scale = top_pca$scale
)
#> <pointer: 0x10f559be0>
# Inspect a lightweight summary without loading the entire matrix
colMeans(scores_fb[, 1:2])
#> [1] 3.944992e-17 3.064216e-17
apply(scores_fb[, 1:2], 2, sd)
#> [1] 1.141546 1.124998To stream the diagnostics into bigmemory-backed
matrices, use the corresponding helper functions:
library(bigmemory)
library(bigPCAcpp)
n <- 1000
p <- 25
bm <- bigmemory::big.matrix(n, p, type = "double")
bm[,] <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), nrow = n)
rotation <- bigmemory::big.matrix(nrow = p, ncol = p)
loadings <- bigmemory::big.matrix(nrow = p, ncol = p)
correlations <- bigmemory::big.matrix(nrow = p, ncol = p)
contrib <- bigmemory::big.matrix(nrow = p, ncol = p)
pca_stream <- pca_stream_bigmatrix(bm, xpRotation = rotation,
center = TRUE, scale = FALSE)
pca_variable_loadings_stream_bigmatrix(rotation, pca_stream$sdev,
loadings)
#> <pointer: 0x138167dd0>
pca_variable_correlations_stream_bigmatrix(rotation, pca_stream$sdev,
pca_stream$column_sd, correlations)
#> Error in pca_variable_correlations_stream_bigmatrix(rotation, pca_stream$sdev, : argument "xpDest" is missing, with no default
pca_variable_contributions_stream_bigmatrix(loadings, contrib)
#> <pointer: 0x1381705f0>Robust workflows dampen the influence of outliers while retaining the
familiar PCA interface. The pca_robust() helper centres
variables by the median, optionally scales by the MAD, and relies on an
iteratively reweighted SVD to derive principal components. The same
robust solver is exposed directly via svd_robust() for use
in custom pipelines, and the streaming-friendly
svd_bigmatrix() wrapper computes classical SVDs on
big.matrix objects without materialising dense copies in
memory.
library(bigmemory)
library(bigPCAcpp)
set.seed(42)
mat <- matrix(rnorm(200), nrow = 40, ncol = 5)
mat[1, 1] <- 15 # introduce an outlier
mat_scaled <- scale(mat, center = TRUE, scale=TRUE)
# Classical PCA on the same data highlights the impact of the outlier
bm_small <- bigmemory::big.matrix(nrow = nrow(mat_scaled), ncol = ncol(mat_scaled), type = "double")
bm_small[,] <- mat_scaled
classical <- pca_bigmatrix(bm_small, center = FALSE, scale = FALSE, ncomp = 3)
classical$explained_variance
#> [1] 0.2940708 0.2332728 0.2031007
scores_classical <- pca_scores_bigmatrix(xpMat = bm_small, rotation = classical$rotation, center = classical$center, classical$scale)
scores_classical[1,]
#> [1] -4.752614 -1.534966 1.578737
pca_plot_contributions(pca_individual_contributions(scores_classical, classical$sdev))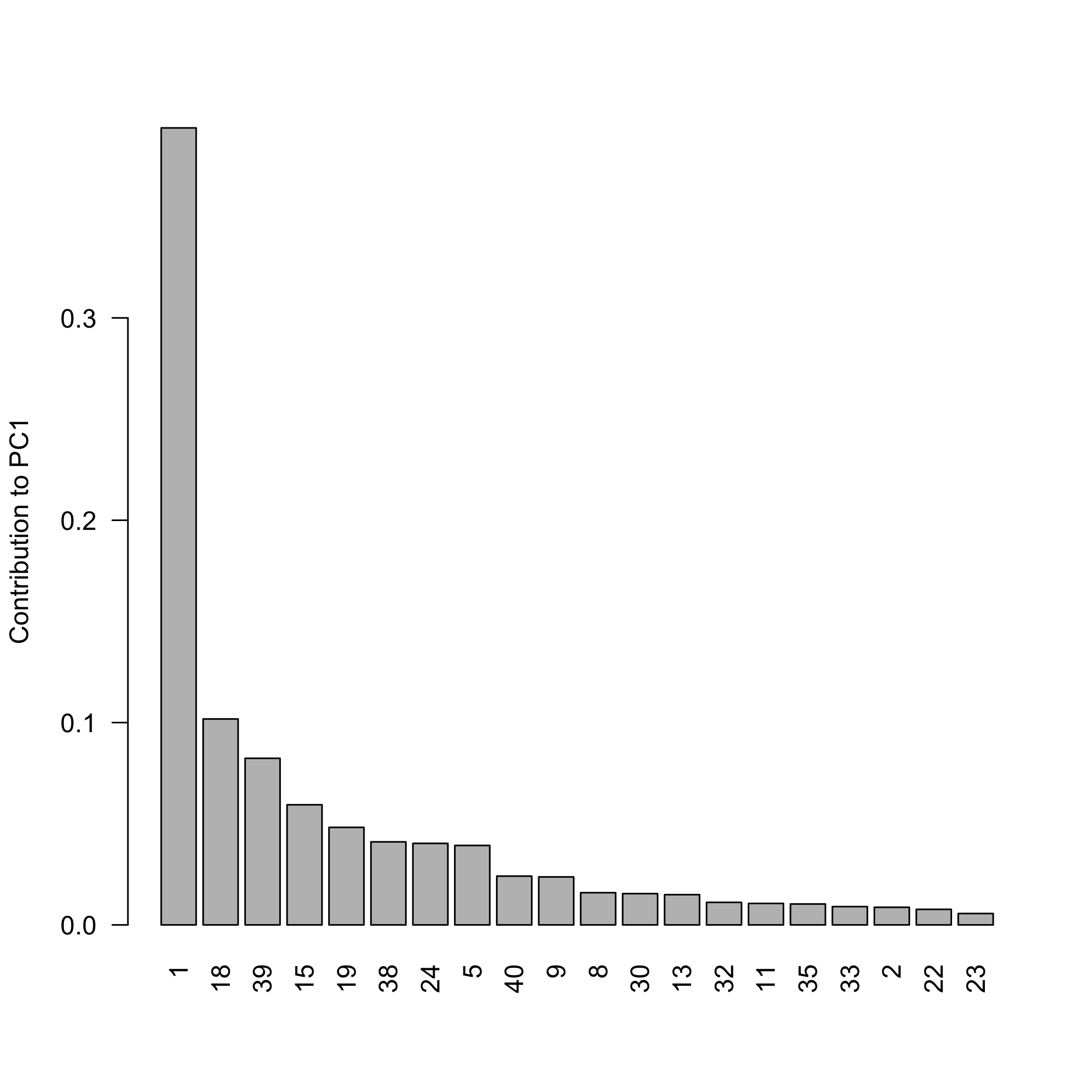
plot of chunk robustsvdexample
# Robust PCA keeps the outlier from dominating the rotation
robust <- pca_robust(mat_scaled, center = FALSE, scale = FALSE, ncomp = 3)
robust$explained_variance
#> [1] 0.3633363 0.3509611 0.2857026
robust$scores[1,]
#> [1] 1.025663 1.948710 2.095546
pca_plot_contributions(pca_individual_contributions(robust$scores, robust$sdev))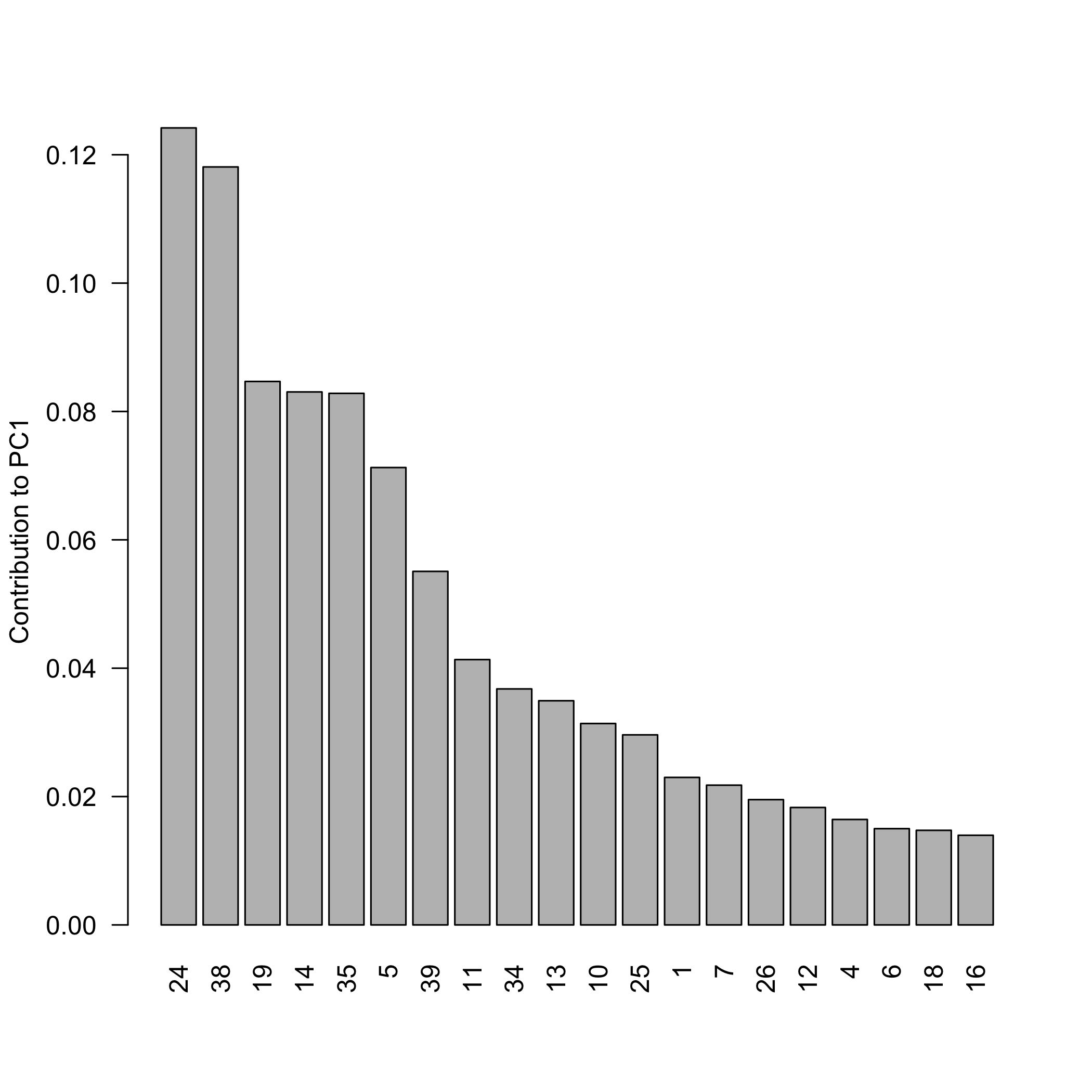
plot of chunk robustsvdexample
cbind(classical = classical$rotation[1:5, 1], robust = robust$rotation[1:5, 1])
#> classical robust
#> [1,] -0.5793644 0.01128235
#> [2,] -0.3121420 0.59547597
#> [3,] -0.5716000 0.77399456
#> [4,] 0.4071138 0.18028142
#> [5,] 0.2728298 0.11709868# Classical SVD on a file-backed big.matrix
path <- tempfile(fileext = ".bin")
desc <- paste0(path, ".desc")
bm <- bigmemory::filebacked.big.matrix(200, 10, type = "double", backingfile =
basename(path), backingpath = dirname(path), descriptorfile = basename(desc))
bm[,] <- matrix(rnorm(2000), nrow = 200)
svd_stream <- svd_bigmatrix(bm, nu = 3, nv = 3)
svd_stream$d
#> [1] 16.66256 15.90085 15.80823 14.84659 13.99062 13.52699 13.06717 12.61343 12.15871 11.63997
# Direct access to the robust SVD routine
svd_out <- svd_robust(mat, ncomp = 3)
svd_out$d
#> [1] 16.789433 6.178555 5.620833
svd_out$weights[1:6]
#> [1] 1 1 1 1 1 1Robust decompositions down-weight the contaminated observations while the classical stream demonstrates how to fetch singular vectors without materialising the dense matrix. The robust solver also exposes per-row weights that can be reused to flag problematic observations for further inspection.
bigPCAcpp bundles plot helpers that operate on both
dense matrices and big.matrix backends. The snippets below
illustrate how to call each function using results from
pca_bigmatrix(). For instance, the
pca_plot_scores() helper samples observations and draws a
scatter plot of their scores on a chosen pair of components, which is
particularly useful when you need to visually assess potential clusters
without loading the full data set into memory.
library(bigmemory)
library(bigPCAcpp)
set.seed(123)
bm <- bigmemory::big.matrix(500, 6, type = "double")
bm[,] <- matrix(rnorm(500 * 6), nrow = 500)
res <- pca_bigmatrix(bm, center = TRUE, scale = TRUE)
# Scree plot of explained variance
pca_plot_scree(res)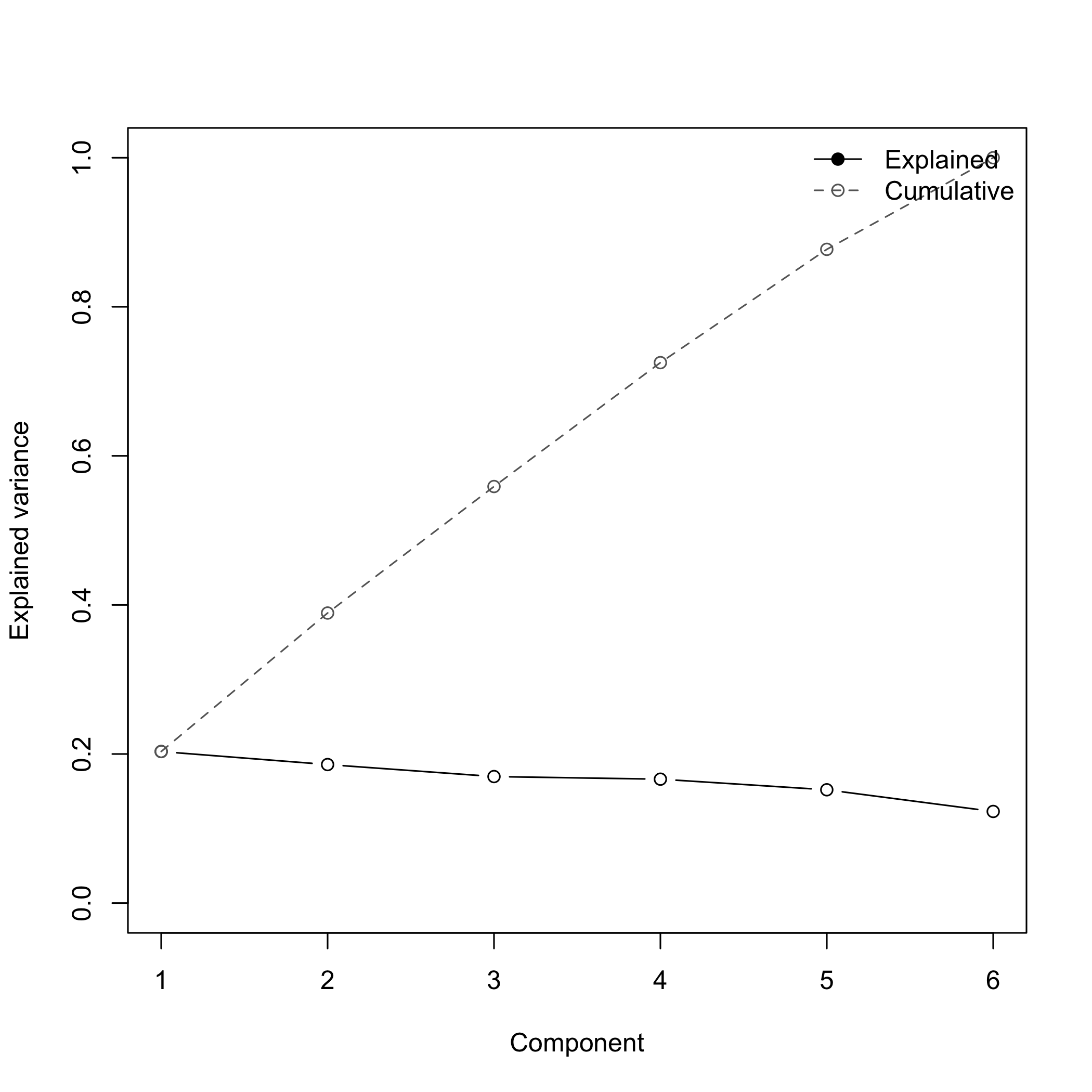
plot of chunk plotexamples
# Scatter plot of sampled scores on PCs 1 and 2
pca_plot_scores(
bm,
res$rotation,
center = res$center,
scale = res$scale,
components = c(1L, 2L),
max_points = 2000L,
seed = 2024
)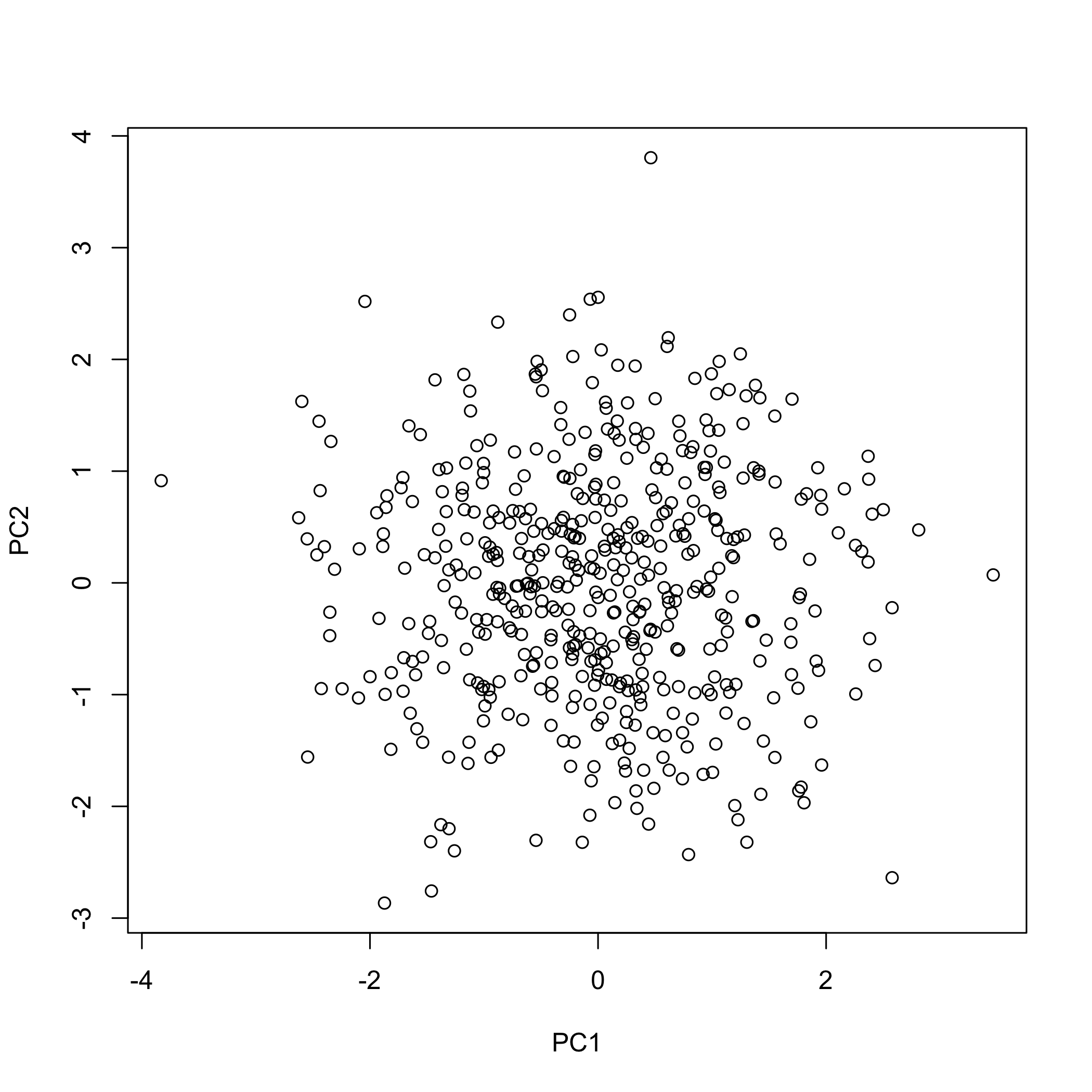
plot of chunk plotexamples
# Contribution bar plot for the leading component
loadings <- pca_variable_loadings(res$rotation, res$sdev)
contrib <- pca_variable_contributions(loadings)
pca_plot_contributions(contrib, component = 1L, top_n = 10L)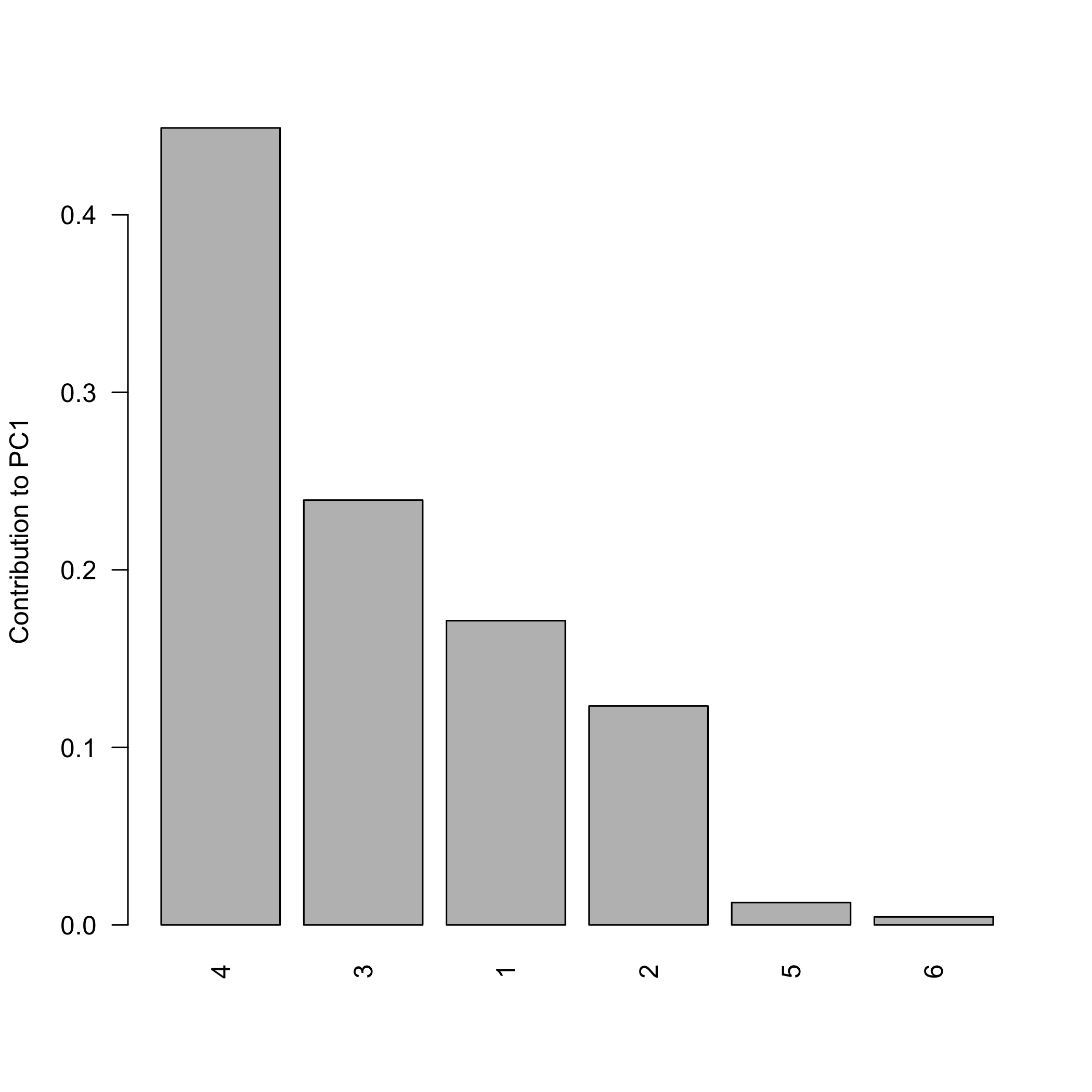
plot of chunk plotexamples
# Correlation circle for the first two components
correlations <- pca_variable_correlations(res$rotation, res$sdev,
res$column_sd, res$scale)
pca_plot_correlation_circle(correlations, components = c(1L, 2L))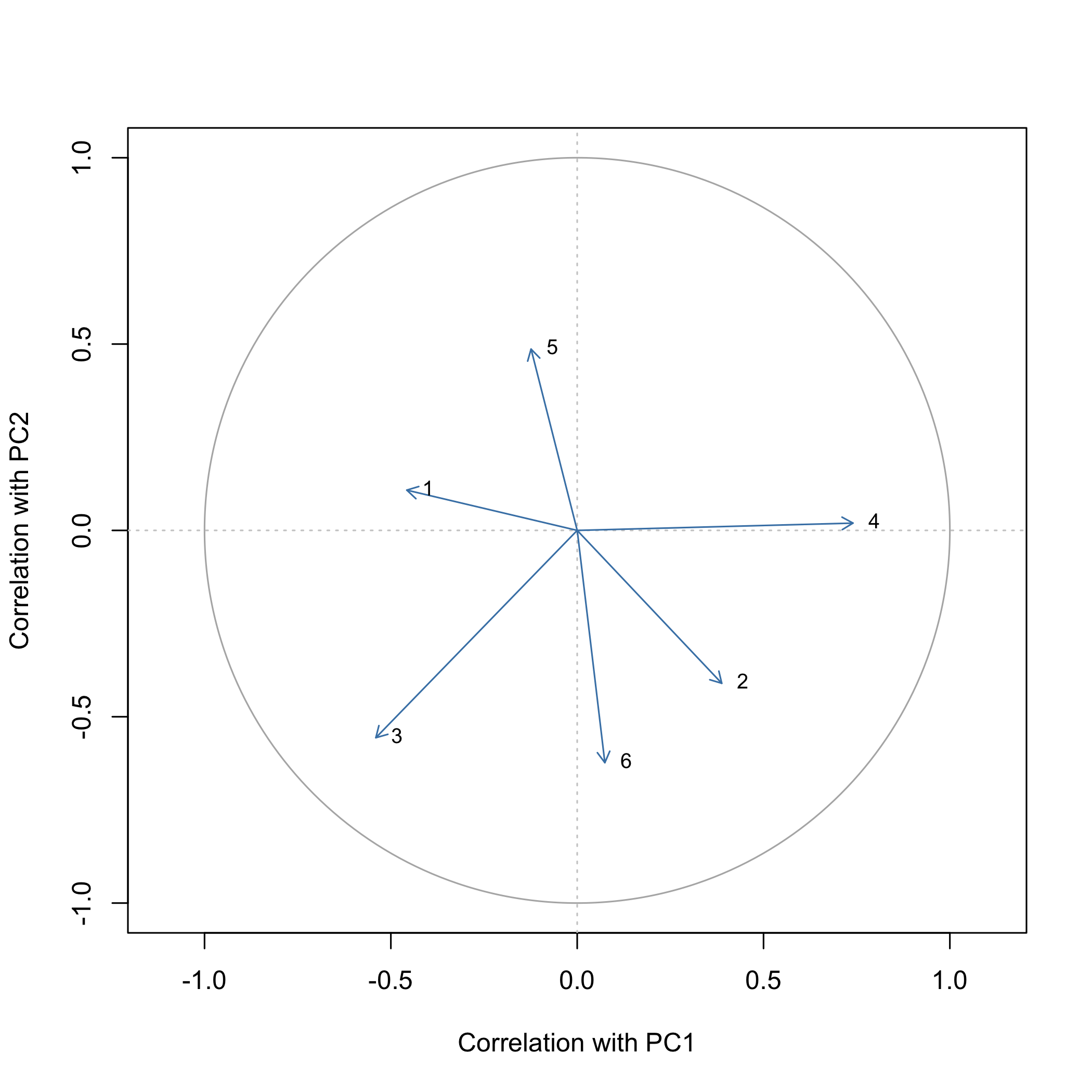
plot of chunk plotexamples
# Biplot combining scores and loadings
scores <- res$scores
if (is.null(scores)) {
scores <- pca_scores_bigmatrix(bm, res$rotation, center = res$center, scale = res$scale)
}
pca_plot_biplot(scores, loadings, components = c(1L, 2L))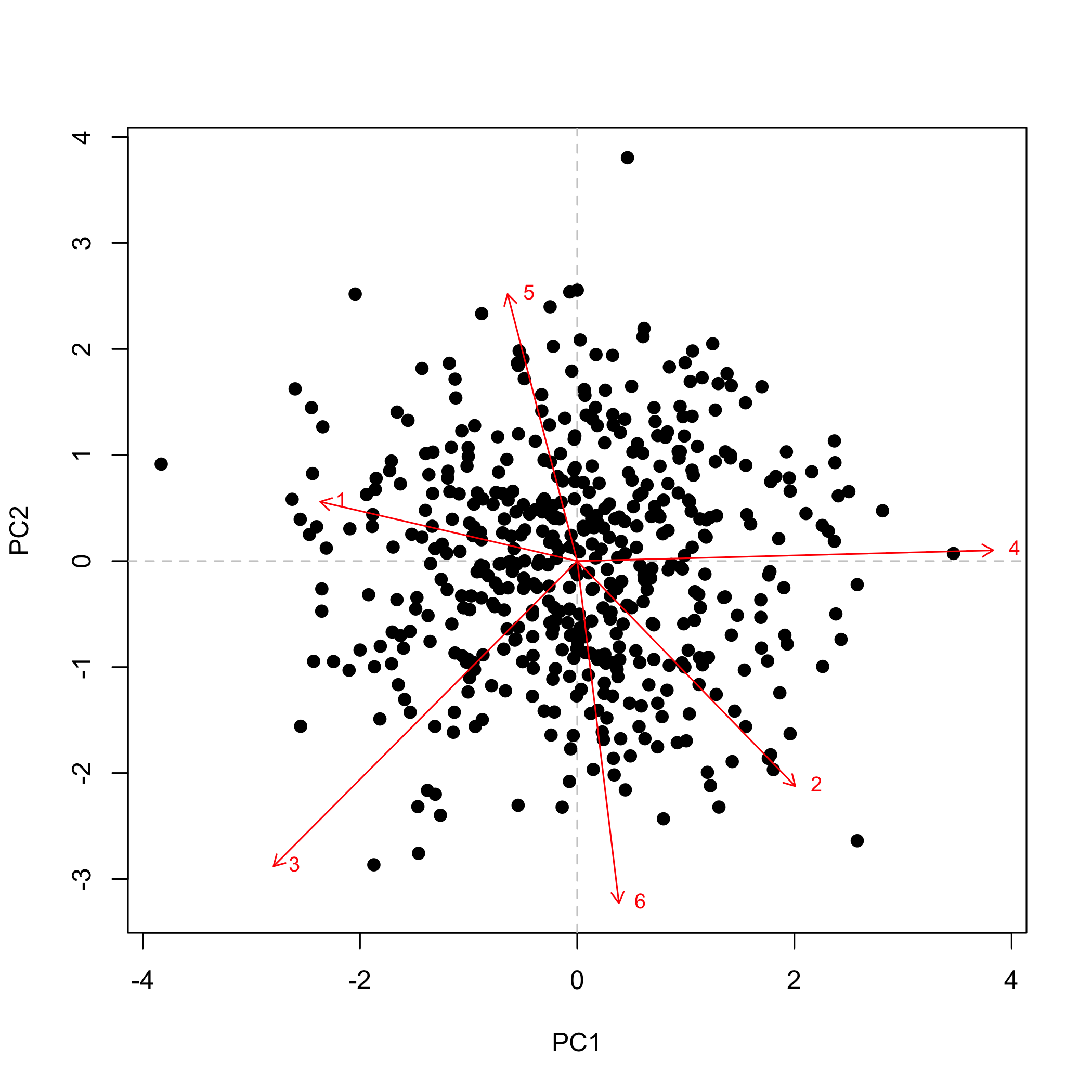
plot of chunk plotexamples
If you use bigPCAcpp in academic work, please cite:
Bertrand F. (2025). bigPCAcpp: Principal Component Analysis for bigmemory Matrices.
Maintainer: Frédéric Bertrand frederic.bertrand@lecnam.net
For questions, bug reports, or contributions, please open an issue on GitHub.